Ultra-fast 99% decomposition of highly concentrated PFAS Sunline develops and commercializes atmospheric pressure plasma technology
株式会社サンライン
Sunline Inc. (Location: 1600-21 Kuga-machi, Iwakuni-shi, Yamaguchi, President: Nobuyuki Kajio), which manufactures and sells fishing lines and other fibers, has developed and commercialized a technology for ultra-fast decomposition of organic fluorine compounds (PFAS) dissolved in liquids using atmospheric plasma. The Plastus Division, which is engaged in R&D, experiments, and equipment development centered on atmospheric pressure plasma technology, has developed and commercialized a technology for ultrafast decomposition of organic fluorine compounds (PFAS) dissolved in liquids using atmospheric plasma.
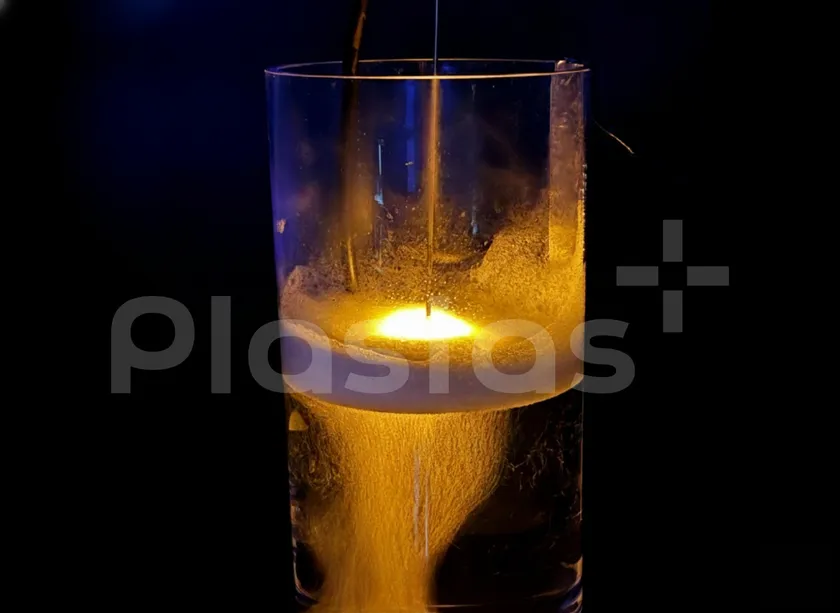

Figure 1: Plasma irradiation
1. background
Organo-fluorine compounds (PFAS) have been widely used in industry for a wide range of applications, including solvents, surfactants, surface treatment agents for textiles, leather, paper, plastics, etc., ion exchange membranes, lubricants, foam extinguishing agents, semiconductor raw materials, and fluoropolymer processing aids, but some PFAS are persistent in the environment (not easily degraded and remaining in soil and water), and some are hazardous for health. However, there are concerns about the persistence of some PFAS in the environment (they do not decompose easily and remain in soil and water) and their impact on human health. However, PFASs are resistant to hydrolysis, photolysis, microbial degradation, and metabolism due to their strong and stable carbon-fluorine bonds, making them difficult to degrade. For example, it is recommended that PFAS-containing wastes be incinerated at temperatures of approximately 1,100°C or higher. (*)
Therefore, although research and demonstration experiments on PFAS decomposition are being conducted by companies and research institutions, technologies that assume large-scale incineration facilities are difficult to apply for research and demonstration purposes, and adsorption and membrane separation technologies leave behind high concentrations of PFAS waste after treatment.
Source: "PFAS Handbook," Office of Organic Fluorine Compounds, Environmental Management Division, Water and Air Environment Bureau, Ministry of the Environment, March 2025.
2. outline of the developed technology
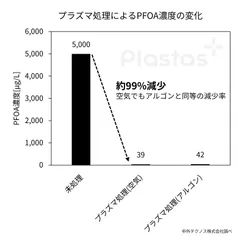
This technology decomposes PFAS by irradiating an aqueous solution containing PFAS with atmospheric pressure plasma (*1) generated by air: (PFOA concentration: 5,000 μg/L before treatment → 39 μg/L after treatment, according to Chugai Technos Co.)
In the past, vacuum facilities or rare gases such as argon were required to generate stable plasma, but with this technology, treatment can be performed under atmospheric pressure and using air as the operating gas, which significantly reduces running costs. By optimizing the processing method and reducing the power consumption of the device for plasma irradiation to approximately 135 Wh, the system can be operated on a 100 V household outlet or portable power supply. Since the system is easy to move and install, it is expected to be installed in existing research facilities and to realize on-site decomposition without transporting the PFAS solution to be treated.
A patent for this technology is pending, and we plan to manufacture and sell the decomposition equipment in the future.
For more information on the technology and equipment, please visit
https://plastas.sunline.co.jp/case/2407/
https://plastas.sunline.co.jp/case/2423/
1 Atmospheric plasma: A collection of electrons and ions ionized by electricity or other energy under one atmosphere above the ground. It is expected to be used in a wide range of fields, such as the decomposition of hazardous substances, because it is extremely chemically active and reacts easily with other substances.
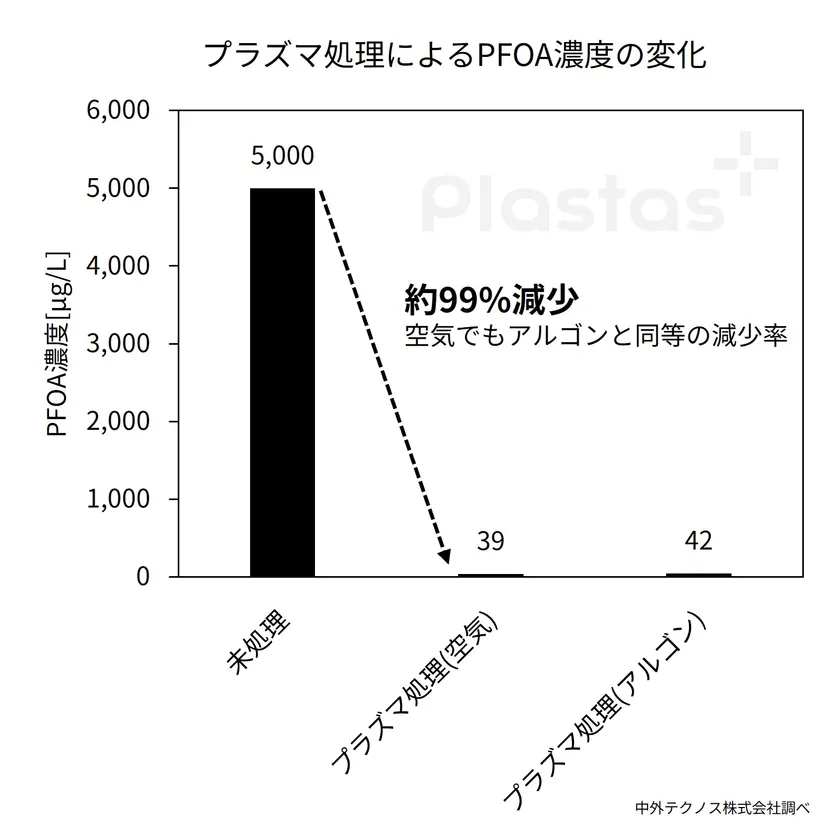
Figure 2: Change in PFOA concentration due to plasma treatment
3. business development
The company will use this technology to launch a PFAS decomposition technology consulting business (analysis of issues related to plasma decomposition of PFAS, planning and testing of technology application methods, custom manufacturing of decomposition equipment, and introduction support, etc.).
This technology is expected to be utilized by researchers and development departments of companies and research institutes as a demonstration base technology to advance research and development of PFAS countermeasures.
4. other
This technology was developed and commercialized using the Yamaguchi Prefecture's "FY2024 Yamaguchi Industrial Innovation Acceleration Grant [Catapult]".
5. company profile
Company name: Sunline Inc.
Representative: Nobuyuki Kajio, President and Representative Director
Location: 1600-21 Kuga-cho, Iwakuni-shi, Yamaguchi 742-0315
Establishment: August 8, 1977
Business activities: Manufacture, processing, and sales of fishing lines for leisure, fishery, and commercial use
Manufacturing, processing and sales of monofilaments for industrial materials
Purchase and sale of various types of fishing tackle
Experimentation, development, processing, and equipment sales of atmospheric pressure and low temperature plasma technology
Capital : 96 million yen
URL : Corporate website https://sunline.co.jp/
Plastus business site https://plastas.sunline.co.jp/
- Category:
- Corporate Trends