The path to medical school abroad. The United States, Italy, Hungary, China, etc. Features of overseas medical schools in 7 countries are disclosed.
MED ITALY株式会社
MED ITALY (Head office: Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo; Representative Director: Shinichiro Kondo), a preparatory school for medical schools in Italy, will release on February 8, 2025 a new article summarizing information on entrance examinations, difficulty levels, and costs in each country to provide the latest information on "medical schools abroad" that are becoming increasingly popular these days. This article will be released on February 8, 2025. This article is based on a feature article in the February 8, 2025 issue of the Weekly Nippon Igaku Shimpo (Japan Medical Journal), which summarizes "characteristics of overseas medical schools" and "information on entrance examinations in major countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom, China, Italy, Germany, Hungary, and the Czech Republic.

Medical Students and Others Studying in a Global Environment
A portion of the article is also excerpted in this article.
The following is from the article "Pursuing Medical School Overseas: Possibilities as a New Option and Differences among Countries.
■ Table of Contents
Competition and Tuition Fees are High Barriers to Medical Schools in Japan
Features of Medical School Admission Abroad
・Medical School Entrance Examinations and Systems by Country/Region
kojutsu: Medical Schools in the U.S.A.
kunitai medical schools
kojutsu chugoku no med school
koMedical Schools in Italy
koMedical Schools in Germany
kojunagari no Igaku (Hungary) no Igaku
kojutsu no med school kojutsu no czechia no med school
For a long time, entering medical school in Japan was considered "the only way to become a doctor," but with the advancement of globalization, more and more students are considering medical school abroad as a new option. Not only do English-language classes and interaction with multinational students broaden international perspectives and provide the impetus to expand career options, but financial benefits may also be available. The Italian medical school prep school, which has partnerships with several universities and provides extensive support for entrance exam preparation and local life after the trip, will provide a thorough explanation of the trends, financial and educational advantages of entering medical school abroad, as well as the features of medical schools in each country and the steps involved in obtaining a medical license in Japan.
------ Competition and Tuition Fees are High Barriers to Medical Schools in Japan
According to statistics released by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) in 2024, there are 81 medical schools in Japan with approximately 120,000 applicants for the 9,500 available positions. The national average acceptance rate is about 8%, which is a very narrow admission gate. Tuition fees are another major hurdle to entry into medical schools in Japan. Tuition at national universities is approximately 3.6 million yen for six years, but the average private university tuition is 32 million yen, and some universities charge more than 40 million yen. In the face of these barriers to medical school admission, a new option is to enter medical school overseas.
------ Characteristics of Medical School Enrollment Abroad
There are four major advantages to attending medical school overseas.
(1) "The entrance examinations are wide open.
Although the focus of entrance examinations differs from country to country, many countries judge each student's aptitude and ability from multiple perspectives, unlike Japanese entrance examinations, which emphasize deviation scores. Because the examinations focus not only on subject test scores but also on individuality and potential, questions that test basic science knowledge and logical thinking are often asked, making the entrance examinations more challenging for students who have difficulty with difficult math and physics problems.
(2) "Relatively inexpensive tuition fees
In Japan, especially at private medical schools, the total tuition for six years averages 32 million yen, which is a high cost to bear. The fact that overseas medical schools have lower tuition fees compared to these schools is a major attraction.
Western Europe (Italy, Germany, France, etc.): about 300,000 yen/year
Eastern Europe (Hungary, Czech Republic, Poland, etc.): about 2 million yen/year
Asia (China, Philippines, etc.): about 1 million yen/year
(3) "It is possible to obtain a Japanese medical license after graduation
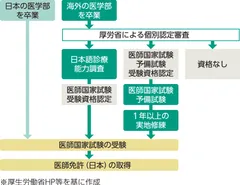
There is no major difference between overseas and domestic universities in terms of what students learn after entering medical school. Even if you studied medicine overseas, you can work as a doctor in Japan if you pass the national medical examination in Japan (Figure 1). When taking the national medical examination, graduates of overseas medical schools are required to undergo an individual examination conducted by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. If they are judged to meet the appropriate standards, they will be eligible to take the national medical examination after undergoing a Japanese language medical examination. On the other hand, if the applicant is judged not to meet the criteria, he/she may be required to take a preliminary examination or undergo on-the-job training for one year or more.
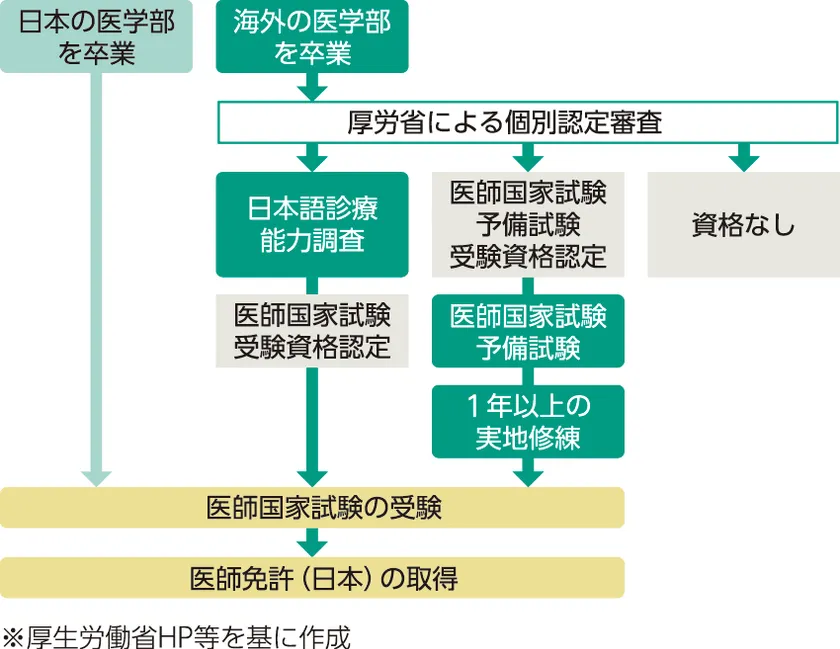
Figure 1) Flow of the National Medical Examination in Japan
(4) "Various Career Paths to Choose From
As mentioned above, you can take the National Medical Practitioners Examination in Japan and work as a doctor in Japan, or you can use your medical license in the country where you graduated and work at a local hospital or medical institution. You can also pursue a career as a doctor or medical professional at international organizations such as WHO or UN Doctors Without Borders.
------ Medical School Admissions and Systems by Country/Region
The level of difficulty of admission, tuition fees, and study environment differ greatly depending on the country or region. While the United States and the United Kingdom, both English-speaking countries, are known for their extremely high level of difficulty in entering medical school, countries that are relatively easy to enter include Hungary, the Czech Republic, and Poland in Eastern Europe, Italy and Malta in Western Europe, and China and the Philippines in Asia. In these countries, information sessions and support systems for Japanese students have been established, and the environment for students wishing to become doctors is much more favorable than in the past.
------ Medical Schools in the U.S.
There are no so-called "medical schools" in American universities, and medical education is conducted in graduate-level "medical schools. However, medical schools are funded by a large amount of taxpayer money, and their basic policy is to give priority to those who will contribute to the U.S. after graduation, and some state universities restrict the admission of foreigners. In addition, the examination process involves a multifaceted screening process that includes grades from college, essays, letters of recommendation, extracurricular activities, tests, and interviews. Tuition fees are extremely high, ranging from approximately 30 to 50 million yen for the university and medical school combined. After graduating from medical school, students must pass the USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination), a three-step national examination (Steps 1-3) to obtain a medical license. The road to becoming a doctor in the U.S. is long and steep, and tuition fees are expensive, so strategic measures such as systematic preparation, information gathering, and scholarships are necessary.
------ Medical Schools in the United Kingdom
Medical school education in the United Kingdom is primarily conducted in English, and for admission by foreigners, a high school diploma and an "A-level" examination or equivalent is required. Language requirements are also strict, with IELTS scores of 7.0 or higher generally required. Tuition fees for international students are approximately 5-7 million yen per year at national universities. Students apply to up to four medical schools through UCAS (Universities and CollegesAdmissions Service), the UK's general application agency, in the fall of each year, and are accepted or rejected based on their scores on the UCAT and BMAT examinations, which are taken between July and October, as well as their application forms, letters of recommendation, and interviews. The acceptance or rejection of an applicant is determined by the applicant's score on the UCAT or BMAT exam, which is taken between July and October, as well as an application form, letters of recommendation, and interview. There are about 40 medical schools in the UK, and graduates can not only work as doctors in the UK, but also in various countries by taking advantage of their medical education in English.
------ Medical Schools in China
Some medical schools in China offer five-year medical programs or oriental medicine depending on the university. If you wish to obtain a medical license in Japan in the future, you need to carefully check whether the curriculum meets the individual screening standards of the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. One of the features of this program is that there are two types of universities, one where students study in Chinese and the other in English. Many universities that have established an administrative office in Japan have a good support system for international students. As an example, at Peking University, classes are mainly in Chinese, but many students travel to Japan after fulfilling language requirements through language study at the office. When entering the university's medical school, students are required to participate in the "Medical School Preparation Course" after being accepted, so that they can learn Chinese and science and math subjects in Tokyo and prepare for life and study there. There are a total of 44 medical schools in English, including Fudan University and Jilin University. Fudan University offers a Western medicine program in English, which attracts many South Asian students. Tuition fees are around 1 to 1.5 million yen at most universities, making it a very good environment for students who are comfortable with learning Chinese, as they can also enjoy the economic benefits.
------ Medical Schools in Italy
There are a total of 21 national and private universities in Italy that offer medical programs in English, with a quota of 960 non-EU international students. The most prestigious national universities, such as the University of Milan and the University of Bologna, offer cutting-edge programs, such as double degrees that allow students to obtain degrees in medicine and engineering at the same time, attracting international students from diverse backgrounds from all over the world in search of a high-level environment. Graduates of Italian medical schools can obtain a medical license valid within the EU, and can work as doctors not only in Italy but also in Germany, France, and other EU countries. The IMAT (Italian National and Public English Medical School Common Admission Test) is used for the entrance examination, and since the test is similar to the Japanese common test, many students apply to both Japanese and Italian universities. Tuition fees are extremely inexpensive compared to private medical schools in Japan, at about 300,000 yen per year for public universities and about 3 million yen for private universities. Another major feature is that the average graduation rate is over 90%.
------ Medical Schools in Germany
In German medical schools, classes are mainly conducted in German. In order for foreigners to be admitted, they must have completed at least two years of education at a university in their home country or have taken a one-year preparatory course after high school graduation, and the language requirements are also strict, requiring a CEFR C1 level of German. The hurdle to admission is very high, as there are few offices in Japan to assist students with the admission process, and students must also complete the admission procedures on their own. Tuition at national universities is free or about 100,000 yen per year, and at private universities, tuition is often inexpensive at about 3 million yen per year. Entrance examinations are mainly based on document screening, and high school grades are important. There are about 35 medical schools in Germany, all of which allow students to apply to more than one school. The most popular universities are Heidelberg, Munich, and Berlin Universities, which rank in the top 30s in the world rankings. After graduation, it is easy to work as a doctor in Germany or in other countries where German is an official language, such as Switzerland and other EU member countries.
------ Hungarian Medical Schools
Hungarian medical schools have started English-language programs from an early stage, and many Japanese graduates are already working as doctors in the EU and abroad. Another attraction of Hungarian medical schools is their low tuition fees, which are approximately 2.5 million yen per year, making them a lighter financial burden compared to private university medical schools in Japan. Currently, four universities in Hungary, Semmelweis University, University of Pécs, University of Szeged, and University of Debrecen, offer medical programs in English, and each university provides a one-year preparatory course to learn the basics of English, biology, chemistry, and physics before admission. The percentage of students who advance from the preparatory course to the regular course is over 90%, allowing students with concerns about their basic academic abilities to take on the challenge with confidence. The entrance examination consists of a first screening and a second screening. The first screening, held about 10 times a year, consists of a written examination (English and two subjects selected from biology, chemistry, or physics) and an interview, while the second screening consists of a written examination (biology, chemistry, or English) and an interview. Each university accepts 25 students for the preparatory course and 5 students for the regular course, which directly leads to the university, for a total of 120 students from the four universities. The study after admission is rigorous, with a straight graduation rate of around 30% for the entire six years, and 1/3 of the students who enroll choose to drop out of school. After graduation, students can obtain a medical license valid in the EU.
------ Medical Schools in the Czech Republic
In the Czech Republic, the National Masaryk University and the National Charles University offer courses at the Faculty of Medicine in English. The first screening, which takes place about five times, consists of a written examination (English and a choice of two subjects from biology/chemistry/physics) and an interview. The second screening, which takes place around mid-April, consists of a choice of three science-related subjects and an interview in English. One of the features of each university is that the annual tuition fee is approximately 2.5 to 3 million yen, which, including living expenses, comes to about 30 million yen over six years. From the third year, students study basic medicine, anatomy, histology, and other subjects in classroom lectures, and from the fourth year, they study a full range of clinical subjects in hospital practical training. The graduation rate for all six years is around 30%.
------ Requires careful information gathering and examination
In today's increasingly internationalized society, entering a medical school not only in Japan but also abroad can be a very effective option for students who wish to become doctors. Studying medicine in English, in particular, will contribute to greatly expanding opportunities for clinical practice and research in Japan and abroad after becoming a doctor in the future. In recent years, an increasing number of countries have established university-accredited administrative offices and are actively accepting students from Japan, making admission to overseas medical schools more accessible than ever before. On the other hand, it is necessary to bear in mind the differences in entrance examination methods and tuition fees between countries, as well as the fact that in some countries the retention and dropout rates are high and graduation is not easy. When considering medical schooling overseas, it will be important to gather accurate information on each country and carefully examine the educational environment and support system in that country.
Future Developments
We hope that this article will help more people become aware of the efforts of MED ITALY Co. Based on our company's philosophy, "One step forward changes the future," we intend to continue to provide even better support for students who wish to enter medical school in Italy, both before and after their trip.
Company Profile
MED ITALY Co.
Representative: Shinichiro Kondo
Location: Tensho Office 8F, 4-16-6 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo
Business description: Operation of a preparatory school, public relations for Italian medical schools, and other support for students in Italy
- Category:
- Corporate Trends
- Genres:
- Education Other Lifestyles Economy(Japan)